Semiconductor Integrated Device & Process Lab.
RRAM
Home  Research
Research  RRAM
RRAM
RRAM
Requirement of New Memory for Improving Computing Performance in Von-Neumann Architecture
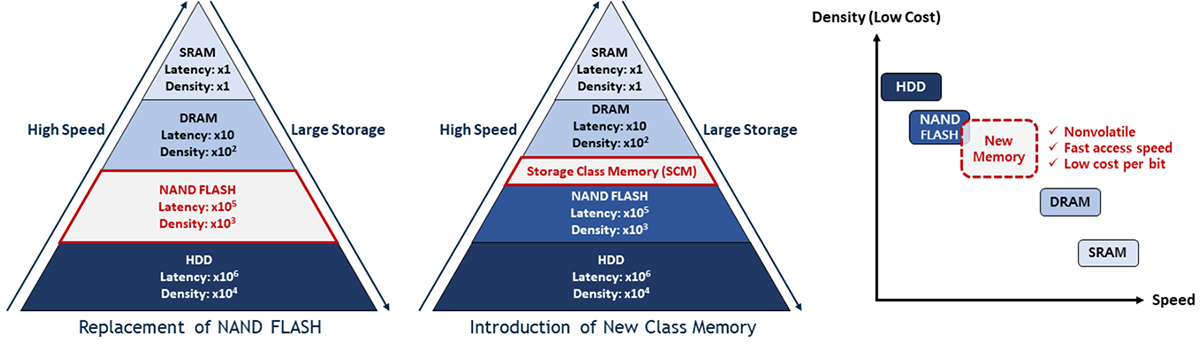
- Latency gap between DRAM and FLASH memory.
- Requirements of SCM: Non-volatility, fast speed, low cost per bit and high density.
- RRAM is one of the most promising memories for SCM thanks to its various advantages.
Resistive Random Access Memory (RRAM)
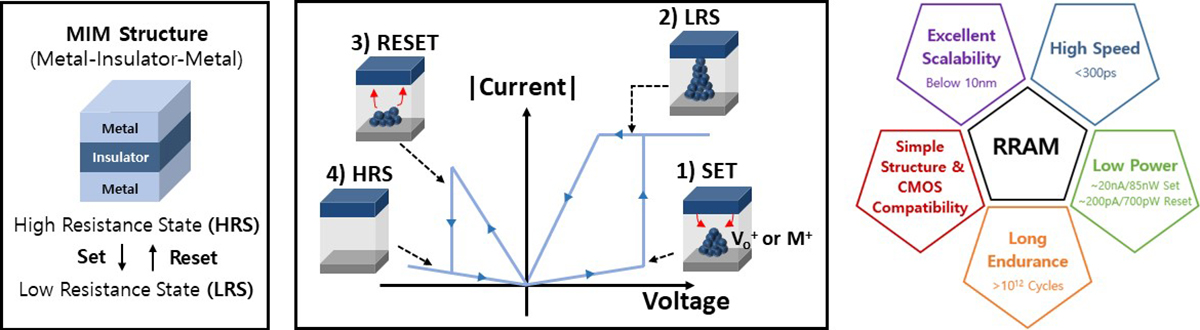
- Metal-insulator-metal (MIM) structure
- External bias changes resistance states (LRS or HRS states) of the insulating layer.
- Advantages of RRAM: Simple structure, excellent scalability, high speed, low power, long endurance and CMOS compatibility.
Types of Resistive Random Access Memory (RRAM)
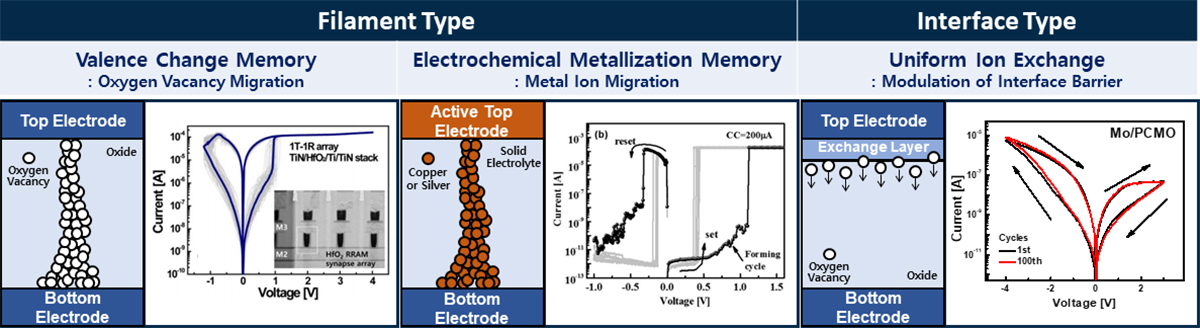
- Filament Type: If conduction path is determined by filaments, formed by gathering of ions moved by external bias.
- Valence Change Memory (VCM): filament based on oxygen vacancy ▶ Relatively good retention
- Electrochemical Metallization Memory (ECM): filament based on metal ions ▶ Extremely high HRS resistance
- Non-filament Type: If conduction path is not confined to filaments consisting of ions.
- Interface type RRAM: Interface barrier modulated by oxygen ions movement ▶ Excellent uniformity
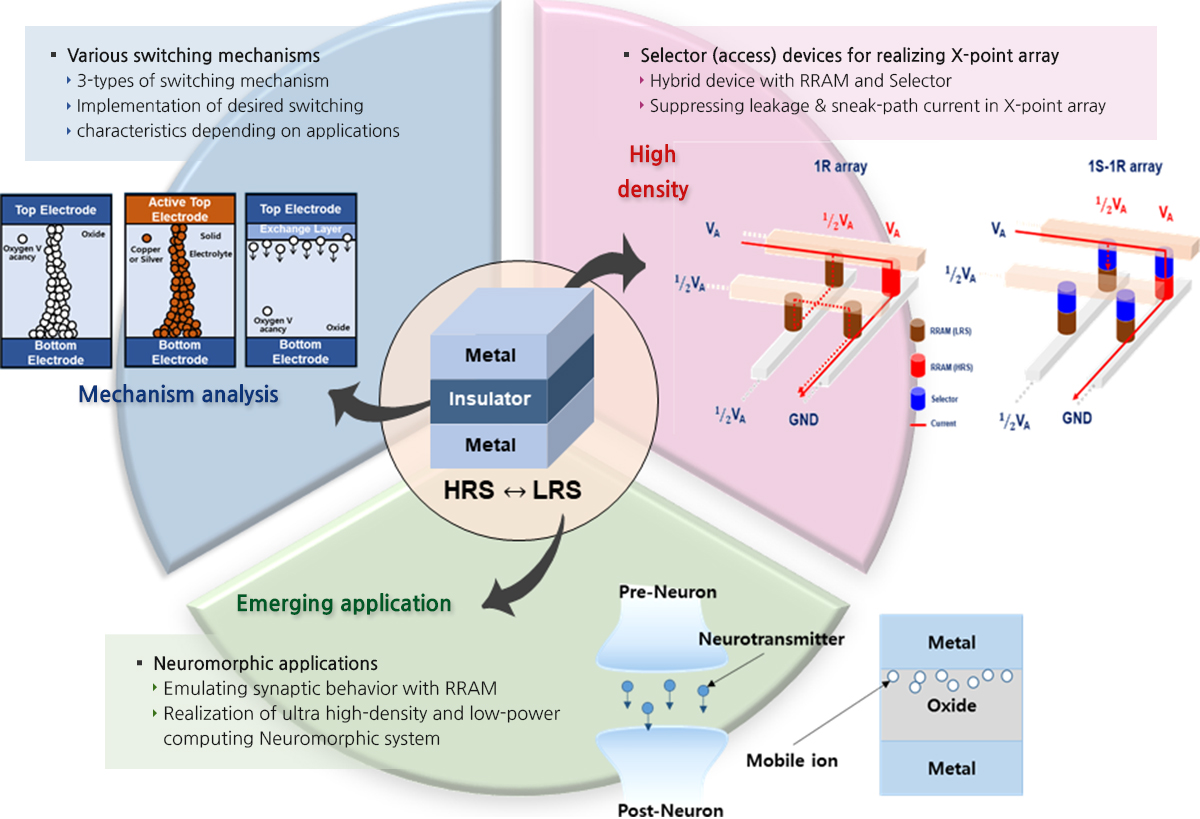
Reference
- 1. J. Woo et al., "Optimized Programming Scheme Enabling Linear Potentiation in Filamentary HfO2 RRAM Synapse for Neuromorphic
Systems." IEEE Transactions on Electron Devices 63.12 (2016): 5064-5067.
- 2. B. Attarimashalkoubeh et al., "Effects of Ti buffer layer on retention and electrical characteristics of Cu-based conductive-bridge
random access memory (CBRAM)." ECS Solid State Letters 3.10 (2014): P120-P122.
- 3. K. Moon et al., "High density neuromorphic system with Mo/Pr0.7Ca0.3MnO3 synapse and NbO2 IMT oscillator neuron." 2015 IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM). IEEE, 2015.